Community articles — Two-column
Recent

his project is part of the FlowNet initiative. FlowNet aims at providing Internet freedom and free flow information through socially informed, censor resistant online social networks. My contribution for FLowNet is in devel- oping an Android application, SecurePost. The requirement for SecurePost is two-fold. First, the system should facilitate secure, anonymous, group communication within a closed group of trusted members. Second, the general public on the Internet viewing this content, should be able to verify that the content was generated only by the said closed group of trusted members. The system consists of an Android client application, a proxy server and a browser-plugin. The OSNs supported by this system are Twitter and Facebook.
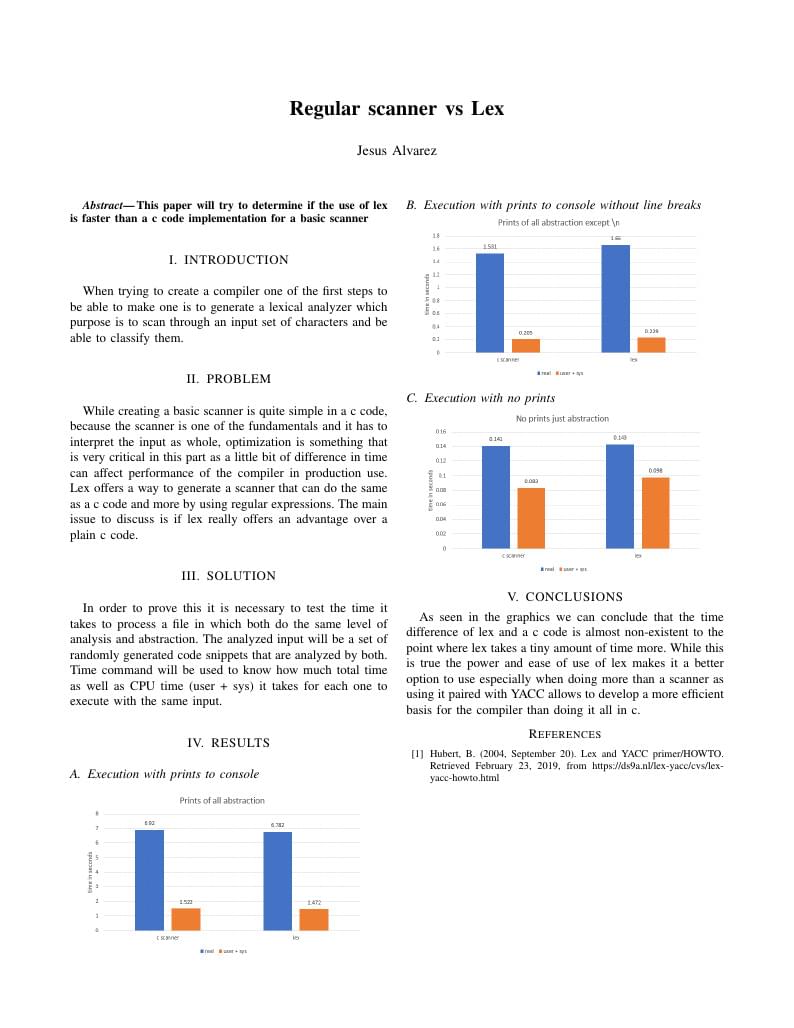
comparison of lex and a c scanner

Created using the Deedy CV/Resume XeLaTeX Template Version 1.0 (5/5/2014)

Con el auge de los sistemas de bases de datos NoSQL los cuales implementan modelos de datos diferentes al relacional como son las bases de datos documentales o de grafos, ha surgido el concepto de Persistencia Políglota. Ésta sostiene que debido a la gran variedad y cantidad de representación de los datos, y los diversos servicios que pueden dar las aplicaciones hoy en día; es necesario el uso de más de un tipo de sistema de almacenamiento para ser capaz de cubrir de forma eficiente todas las necesidades de la aplicación que use dicho sistema. En este trabajo se busca dar una idea general de las Aplicaciones de Persistencia Políglota describiendo las posibles arquitecturas que hacen uso de las bases de datos NoSQL y su funcionamiento, se estudian algunos casos de éxito y se lleva a cabo un caso de estudio usando MongoDB y Neo4j.

Created using the Deedy CV/Resume XeLaTeX Template Version 1.0 (5/5/2014) This template has been downloaded from: http://www.LaTeXTemplates.com Original author: Debarghya Das (http://www.debarghyadas.com) With extensive modifications by: Vel (vel@latextemplates.com)

En este documento se muestra un acercamiento identificación de especies arbóreas mediante Histogramas De Gradientes Orientados y maquinas de soporte Vectorial.
O programa detalhado a seguir apresenta a jogo da cobrinha implementado em Assembly MIPS
With Overleaf, edit online instantly this IET Electronics Letters Journal example and download a PDF version. This project is also available on my web site

Classifying pulmonary nodule CT images as either benign or malignant, using a trained Residual Neural Network.
\begin
Discover why over 25 million people worldwide trust Overleaf with their work.